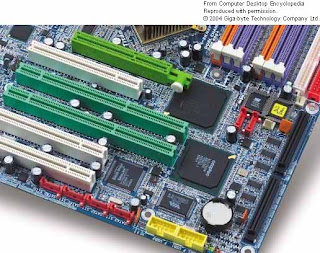
Intel introduced the PCI bus architecture in the early 1990s, and
the PC expansion bus was never again the same. Intel made many smart moves
with PCI, not the least of which was releasing PCI to the public domain to make
it very attractive to manufacturers. PCI provided awider, faster,more flexible alternative
than any previous expansion bus. The exceptional technology of the
new bus, combined with the lack of a price tag, made manufacturers quickly
drop ISA and the other alternatives and adopt PCI.
PCI really shook up the PC world with its capabilities. The original PCI bus
was 32 bits wide and ran at 33 MHz, which was superb, but these features were
expected and not earth-shattering. The coolness of PCI came from its ability to
coexist with other expansion buses.When PCI first came out, you could buy a
motherboard with both PCI and ISA slots. This was important because it enabled
users to keep their old ISA cards and slowly migrate to PCI. Equally impressive
was that PCI devices were (and still are) self-configuring, a feature that
led to the industry standard that became known as Plug and Play (PnP). Finally,
PCI had a powerful burstmode feature that enabled very efficient data transfers.
AGP
Shortly after Intel invented PCI, the company presented a specialized, videoonly
version of PCI called the accelerated graphics port (AGP). An AGP slot is a
PCI expansion bus slots PCI slot, but one with a direct connection to the Northbridge. AGP slots are
only for video cards—don’t try to snap a sound card or modem into one.
. An AGP slot is almost universally brown in
color, making it easy to spot.
PCI-X
PCI-X, already available in systems such as the Macintosh G5, is a huge
enhancement to the current PCI technology that is also fully backwardcompatible,
in terms of both hardware and software. PCI-X is a 64-bit-wide bus
Its slots will accept regular PCI cards. The real bonus of
PCI-X is its much enhanced speed. The PCI-X 2.0 standard features four speed
grades (measured in MHz): PCI-X 66, PCI-X 133, PCI-X 266, and PCI-X 533.
Mini-PCI
PCI has even made it into laptops in the specialty Mini-PCI format . You’ll findMini-PCI in just about every laptop these days.Mini-PCI
is designed to use low power and to lie flat⎯both good features for a laptop
expansion slot.
PCI Express
PCI Express (PCIe) is the latest, fastest, and most popular expansion bus in use
today. As its name implies, PCI Express is still PCI, but it uses a point-to-point
serial connection instead of PCI’s shared parallel communication. Consider a
single 32-bit chunk of data moving from a device to the CPU. In PCI parallel
communication, 32 wires each carry 1 bit of that chunk of data. In serial communication,
only one wire carries those 32 bits. You’d think that 32 are better
than 1, correct?Well, first of all, PCIe doesn’t share the bus.A PCIe device has its
own direct connection (a point-to-point connection) to the Northbridge, so it
does not wait for other devices. Plus, when things start going really fast (think
gigabits per second), it’s difficult to get all 32 bits of data to go from one device
to another at the same time because some bits get there slightly faster than
others. That means you need some serious, high-speed checking of the data
when it arrives to verify that it’s all there and in good shape. Serial data doesn’t
have this problem, as all the bits arrive one after the other in a single stream.
When data is really moving fast, a single point-to-point serial connection is
faster than a shared, 32-wire parallel connection.
And is PCIe fast! A PCIe connection uses one wire for sending and one for
receiving. Each of these pairs of wires between a PCIe controller and a device is
called a lane. Each lane runs at 2.5 Gbps. Better yet, each point-to-point connection
can use 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, or 32 lanes to achieve a maximum bandwidth
of 160 Gbps. The effective data rate drops a little bit because of the encoding
scheme—the way the data is broken down and reassembled—but full duplex
data throughput can go up to a whopping 12.8 GBps on a ×32 connection.
The most common PCIe slot is the 16-lane (×16) version most commonly
used for video cards The first versions of PCIe
motherboards used a combination of a single PCIe ×16 slot and a number of
standard PCI slots. (Remember that PCI is designed to work with other expansion
slots, even other types of PCI.)
Local Lingo
PCIe When you talk about the lanes, such as ×1 or ×8, say “by” rather
than “ex” for the multiplication mark. So “by 1” and “by 8” are the correct
pronunciations. You’ll probably hear it referred to as “ex 8” and “8 ex”
for the next few years until the technology has become a household term.
The bandwidth generated by a ×16 slot is far more than anything other than
a video card would need, so most PCIe motherboards also contain slots with
fewer lanes. Currently ×1 and ×4 are the most common general-
purpose PCIe slots, but PCIe is still pretty new so expect things to change
as PCIe matures.